(Pre-warning of Imports and Exports)
According to Customs statistic, China imported 699,000t sugars in the first three quarters of the year, registering a drop of 28.1% compared with that of the same period last year (the same below), with a total value of USD 280 million and a mean import price of USD 404.8/t that are a drop of 7.9% and an increase of 28.1% respectively. In September alone, imported sugars amounted to 44,000t, registering a drop of 69.5%, with a value of USD 18.92 million and a mean import price of USD 427.2/t that are a drop of 59.6% and an increase of 32.5% respectively. Sugar imports have the following main characteristics:
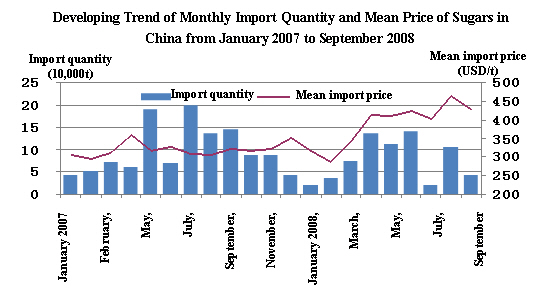
I. Mean import price has been on a steady up trend. In February, China’s mean sugar import price once fell below USD 300/t to USD 287.2/t which rebounded to USD 343.7/t in March. The price surged higher thereafter and reached as high as USD 461.8/t in August and then it came down to USD 427.2/t in September, still well above USD 400/t (see the following figure).
II. Sugars are imported primarily through general trade. In the first three quarters, China imported 567,000t sugars through general trade, registering a drop of 31% and accounting for 81.2% of total sugar imports in the same period. Meanwhile, sugar imports through processing trade amounted to 80,000 tons, registering a drop of 24% and accounting for 11.4% of total sugar imports.
III. State-owned enterprises account for 70% of the total imports. In the first three quarters, state-owned enterprises imported 474,000t sugars, registering a drop of 19.5% and accounting for 67.9% of total sugar imports of China. In the meantime, private enterprises imported 151,000t sugars, registering a drop of 42.7% and accounting for 21.6% of total sugar imports of China. Foreign-funded enterprises imported 59,000t sugars, registering a drop of 41.8%.
IV. Cuba, India and Korea are the main sources of imports. China signed a long-term raw sugar supply agreement with Cuba for an annual supply of 400,000t raw sugars. In the first three quarters, China imported 383,000t sugars from Cuba, registering a growth of 14.4% and accounting for 54.7% of China’s total sugar imports. In the meantime, China imported 160,000t and 89,000t sugars from India and Korea respectively, registering a growth of 190% and 22.7% respectively and accounting for 22.9% and 12.7% of China's total sugar imports respectively.
It is noteworthy that China’s sugar output has seen rapid growth and that results in a more serious oversupply and substantial price drop in the domestic market. For that reason, farmer interests may be damaged by such price drops. According to the statistics of China Sugar Association, China had a sugar inventory of 1.5 million tons for the 2007/2008 production year as of September, the biggest addition of new stocks in history. The sugar import quantity only accounted for 35.9% of the import quotas (1.945 million tons) for 2008 that is a fall of 14 percentage points compared with that of the same period last year. The situation of oversupply sees no reversal. In the meantime, sugar prices in the domestic market fell dramatically, with Zhengzhou Exchange Sugar 901 Contract price falling from RMB 5,385/t on March 4 down to RMB 2,652/t on October 10, or a drop of over 50% within just seven months. The prevailing 905 Contract price also fell from RMB 4,145/t on June 19 down to RMB 2,789/t on October 10, or a drop of over 30%. The international sugar market is basically occupied by Cuba and Brazil currently and China’s sugar products are not competitive enough. In the first three quarters of the year, China exported only 42,000t sugars, registering a substantial drop of 58.1%. For that reason, the oversupply in the domestic market can’t be alleviated through exports.
Proposals (omitted)

